
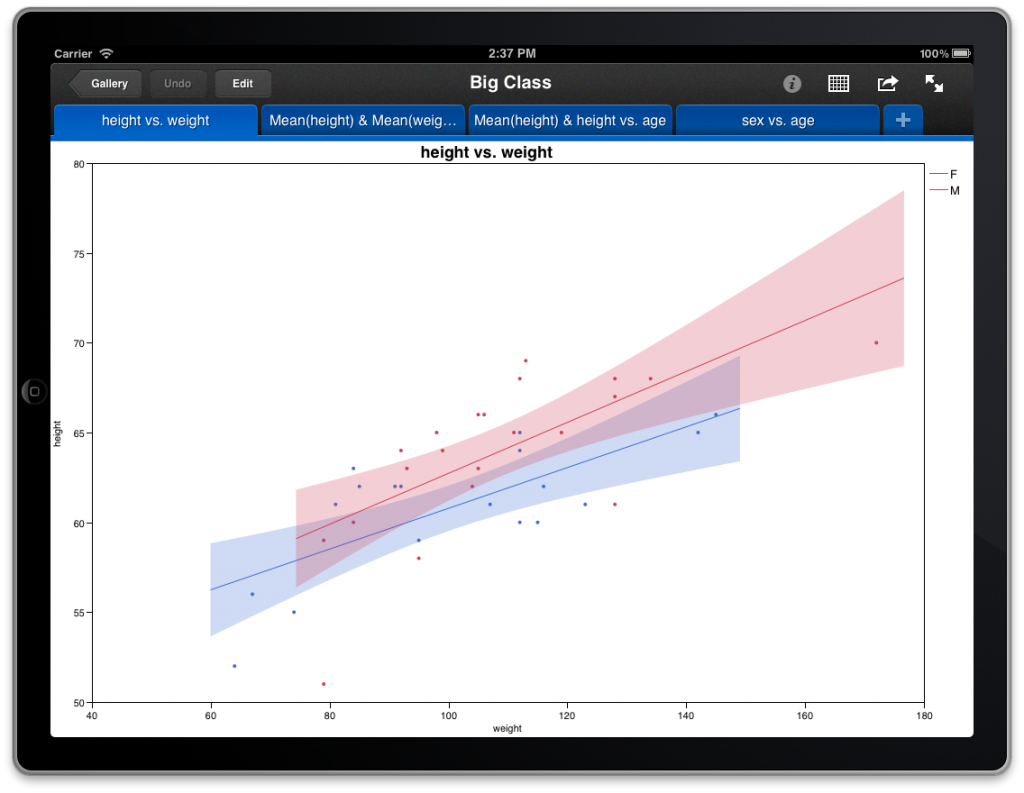
You might find it helpful to use both types of graphs with your data. These data points are worthy of review to determine if they are outliers or errors the whiskers will not include these outliers. These points are often called outliers. An outlier is more extreme than the expected variation. If the data do not extend to the end of the whiskers, then the whiskers extend to the minimum and maximum data values. If there are values that fall above or below the end of the whiskers, they are plotted as dots. The whiskers represent the expected variation of the data. The whiskers extend 1.5 times the IQR from the top and bottom of the box. The lines that extend from the box are called whiskers.The length of the box is the difference between these two percentiles and is called the interquartile range (IQR). These two quantiles are also called quartiles because each cuts off a quarter (25%) of the data. The bottom and top of the box show the 25 th and 75 th quantiles, or percentiles.If the data are skewed, the median will be closer to the top or to the bottom of the box. If the data are symmetrical, the median will be in the center of the box. Half of the data is above this value, and half is below. The center line in the box shows the median for the data.See the "Comparing outlier and quantile box plots" section below for another type of box plot. Either way, you are simply naming the different groups for the data.The term “box plot” refers to an outlier box plot this plot is also called a box-and-whisker plot or a Tukey box plot.
#Jmp graph builder histogram count percent code
You can use the country abbreviation, or you can use numbers to code the country name. Country of residence is an example of a nominal variable. With nominal data, the sample is also divided into groups but without any particular ordering. For example, in a survey where you are asked to give your opinion on a scale from “Strongly Disagree” to “Strongly Agree,” your responses are categorical. With categorical data, the sample is often divided into groups and the responses have a specific ordering. Histograms do not make sense for categorical or nominal data since they are measured on a scale with only a few possible values. Categorical or nominal data: use bar charts Some examples of continuous data are:įor all of these examples, a histogram is an appropriate graphical tool to explore the distribution of the data. Histograms make sense for continuous data since they are measured on a scale with many possible values. Histograms and types of data Continuous data: appropriate for histograms With some software, you can explore group differences in a single histogram, as is shown in the figures above. If there is a possibility of groups, you are likely to learn more about the data by creating separate histograms for each group. These graphs help identify an important consideration: whenever you create a histogram, think about whether or not there are groups in your data. However, it is harder to see the overall shape than in the first figure. You can still see the center, spread, and shape of the data.
#Jmp graph builder histogram count percent software
However, some software tools allow you to change the number of bins and bin starting points, which allows you to explore and better understand your data.įigure 2 shows the same data as in Figure 1 but with many more bars. With software, the bins are defined by the program. The bar height then shows the number of people in each decade.
For example, to create a histogram for age in years, you might decide on bins by decade (0-10, 11-20, and so on). With equal bins, the height of the bars shows the frequency of data values in each bin. Most of the time, the bins are of equal size. To generate a histogram, the range of data values for each bar must be determined. The bars represent the measured values for each category.
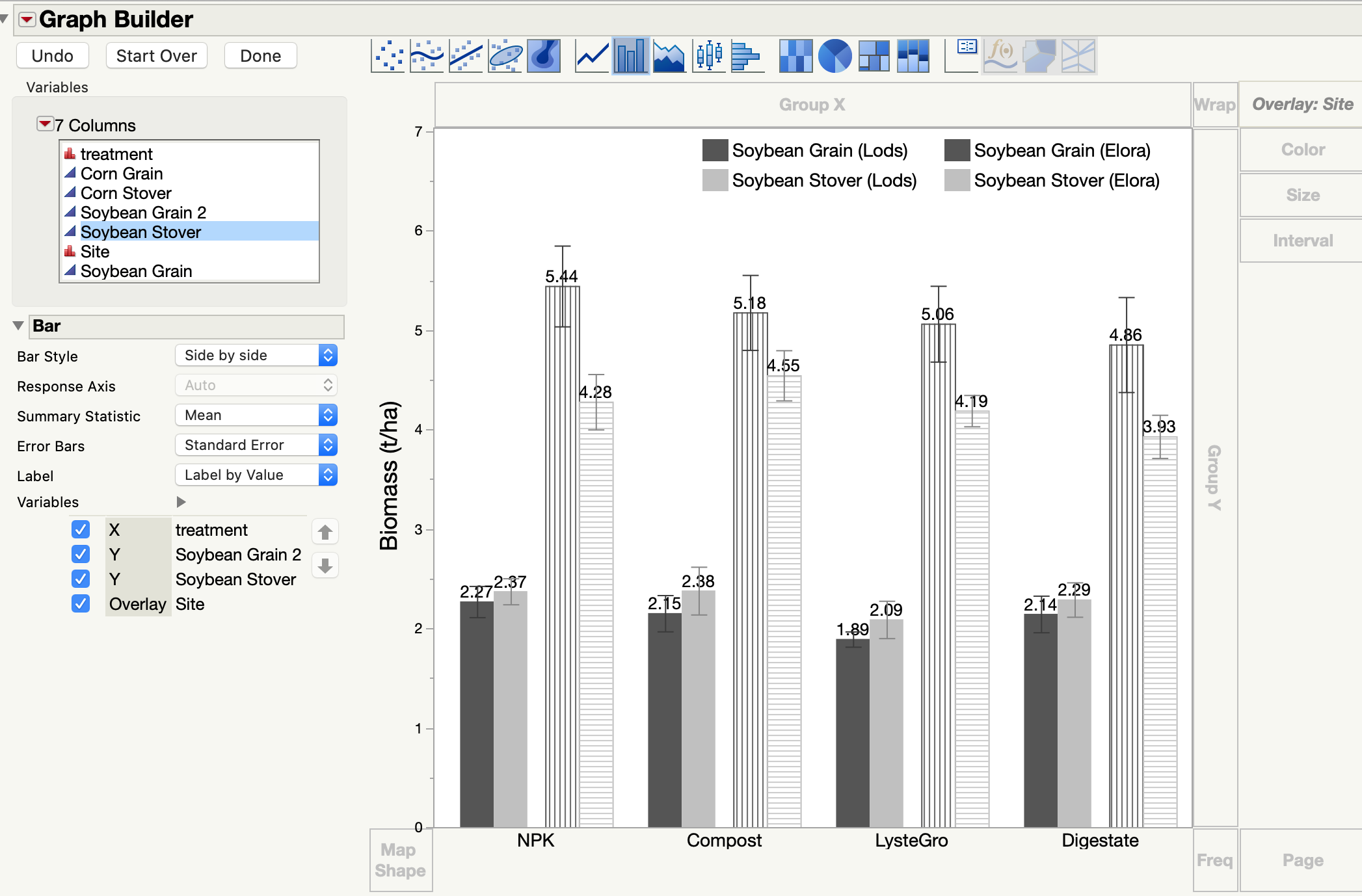
The bars represent the number of values occurring within a range specified on the horizontal axis. Histograms do not have gaps between bars. Histograms are used with continuous data, while bar charts are used with categorical or nominal data. The key difference between histograms and bar charts is the type of data that is being plotted. What is the difference between histograms and bar charts?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
